Auralin-clinical-trial
(Disclaimer: The clinical dataset is fabricated for the sake of data wrangling practice on Udacity. It is constructed to simulate real-world dataset with the consults of real doctors. The ‘auralin’ and ‘novodra’ are NOT real insulin products, however, it mimics the real clinical trial for an inhaled insulin, Afrezza.)
Introduction
The increasing prevalence of diabetes in the 21st century is alarming. Diabetes is a persistently elevated blood sugar level due to the inability to produce sufficient insulin or the inability of the body to use its own insulin.
Diabetes, although not curable, can be managed effectively with insulin. However, insulin can only be administered by a needle multiple times daily because of the unfavorable stomach condition. Won’t there be better compliance if there is an oral insulin tablet?
In this phase II clinical trial, I compare the effectiveness of Auralin, an oral Insulin, using Novodra, a popular injectable insulin, as a standard.
Problem Statement/ Hypothesis
Auralin, an oral insulin, will demonstrate comparable efficacy in glycemic control to Novodra, the injectable Insulin while offering greater patient compliance and convenience due to its oral form. The study aims to determine whether Auralin’s oral delivery method can achieve similar or superior results in managing blood glucose levels compared to Novodra
Skills and Tools Used
- Programming Language: Python
- Project Management: Trello Board
- Statistical modeling
- Data Manipulation
- Data Visualization
- Data Cleaning
- Communication
- Report writing
Task Overview
Here is a concise high-level review of the critical tasks to achieve the project goal.
- Loaded and reconciled the dataset into a single table.
- In-depth exploration, manipulation, and handling of data quality and structural issues such as missing values, duplicated entries, wrong formatting, etc.
Duplicated Entries
A comprehensive examination for duplicate entries shows John Doe is a single patient with six different patient ID.
Structural Anomaly
Three distinct features: ‘treatment’, ‘start_dose’ and ‘end_dose’ are reported as two features: ‘auralin’ and ‘novodra’.
Cleaned Dataset
Following the comprehensive cleaning process aimed at addressing the identified dataset issues, here are the resultant outcomes.
- Visualized relationship between features of interest for insightful pattern and enhanced the pattern by engineering new features.
- Performed statistical analysis to test the hypothesis.
Insights / Outcomes
Below are some of the remarkable insights gleaned from the analysis.
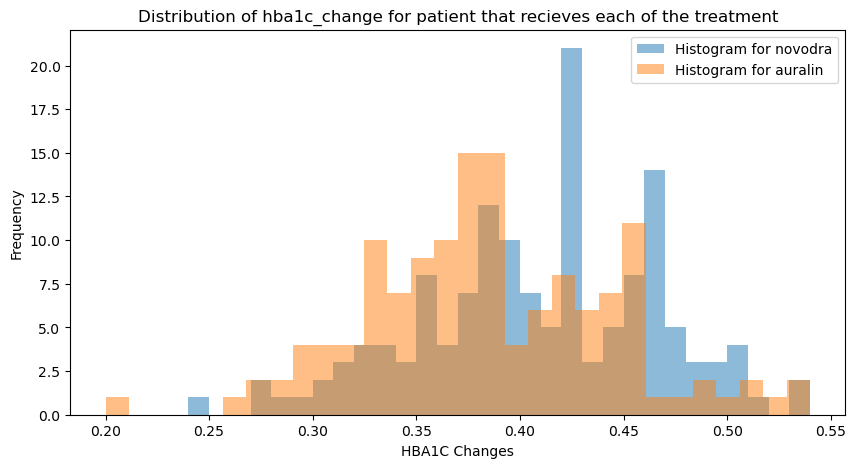
Do patients on Auralin have higher glycemic control than those on Novodra?
A statistically significant difference (t = 3.08, p = 0.002, $\alpha$ = 0.05) in HbA1c changes between Novodra and Auralin treatments. Therefore, we reject the null hypothesis, concluding that Novodra leads to a significantly greater HbA1c change than Auralin.
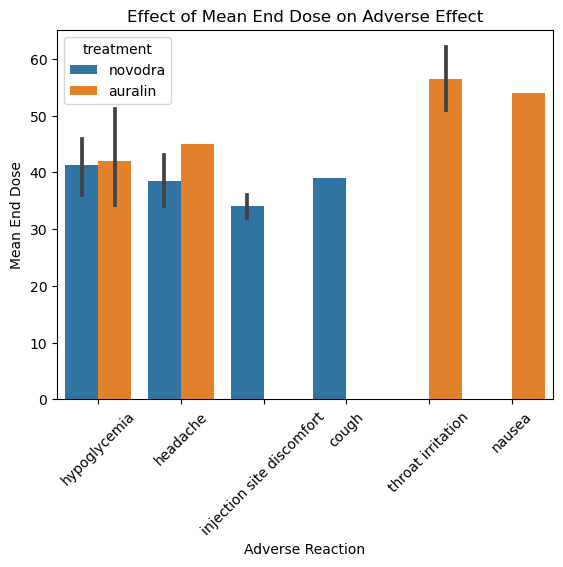
Are adverse effects observed depending on the dose of aural or no vodka?
Many of the side effects are a result of the model of administration: throat irritation and nausea for Auralin and injection site discomfort for Novodra. However, the common side effects of headache and hypoglycemia are reported in more patients taking Auralin compared to Novodra.
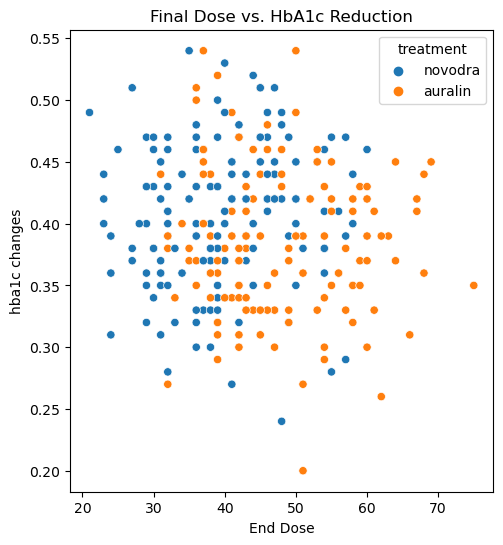
Does an increased dose of auralin or Novodra translate to increased HbA1c Reduction?
There is an inverse relationship between the dosage of auralin (Corr. Coef. = -0.0730) and its corresponding impact on the HbA1c levels, whereas Novodra (Corr. Coef. = 0.0898) demonstrates a direct proportional relationship with the response. Using the minimum effective dose of auralin can mitigate the side effects.
Ready to unlock the full potential of your data? I’m excited to collaborate and help your business thrive through data-driven insights. Get in touch!


